
Differentiated Generics
Discover how Norbrook is improving customer access to affordable, differentiated generic drugs
Quality you can trust
A generic drug is bioequivalent to the pioneer product and Norbrook has decades of experience in manufacturing the highest quality generic drugs. Our manufacturing facilities have been audited and approved by the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA), Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) and European Medicines Authority (EMA).
Norbrook is committed to improving the access and affordability of generic animal pharmaceuticals to veterinarians, farmers and pet owners around the world. Our portfolio spans a number of therapeutic categories and is on sale in over 100 countries worldwide. Our generic drugs work in the same way and provide the same clinical benefits as their brand-name counterparts.
Your questions answered
Generic Drugs FAQs
What's the difference between generic and branded drugs? Do they work the same way? Read our FAQs here to get all the answers.
-
What is a generic drug?
A generic drug displays pharmaceutical equivalence or bioequivalence to the pioneer product.
The generic product has the same qualitative and quantitative composition of active substances, and the same pharmaceutical form as the reference product (pharmaceutical equivalence). Alternatively, bioequivalence with the reference medicinal product has been demonstrated by bioavailability studies.1
-
Are generics manufactured to the same high quality standards?
Generic drugs are equivalent to pioneer drugs
According to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) licensing process, the generic manufacturer must show that the generic drug is equivalent in quality, safety and efficacy to the approved
pioneer (“Brand”) drug in:- Active ingredient
- Strength
- Dosage form
- Dosage regime

In addition:
• Each ingredient must meet stringent quality standards
• The generic must demonstrate stability for the shelf life of the product -
Are generics equivalent to the pioneer?
EMA regulated manufacturing standards are identical
Pioneer drugs and generic drugs must be manufactured to the same high quality standards set out by the EMA2.
Both are manufactured in Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) accredited facilities, to comply with the principles of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in relation to Manufacturing Authorisations (ManA).
-
Do pioneer drugs go through more testing?
If a product is not pharmaceutically equivalent, bioequivalence has to be proven
Blood level bioequivalence (BE) studies compare a test product (generic drug) to a reference product (pioneer drug) using parameters measuring and encompassing:
-
Absorption
-
Distribution
-
Depletion of the drug concentration over time
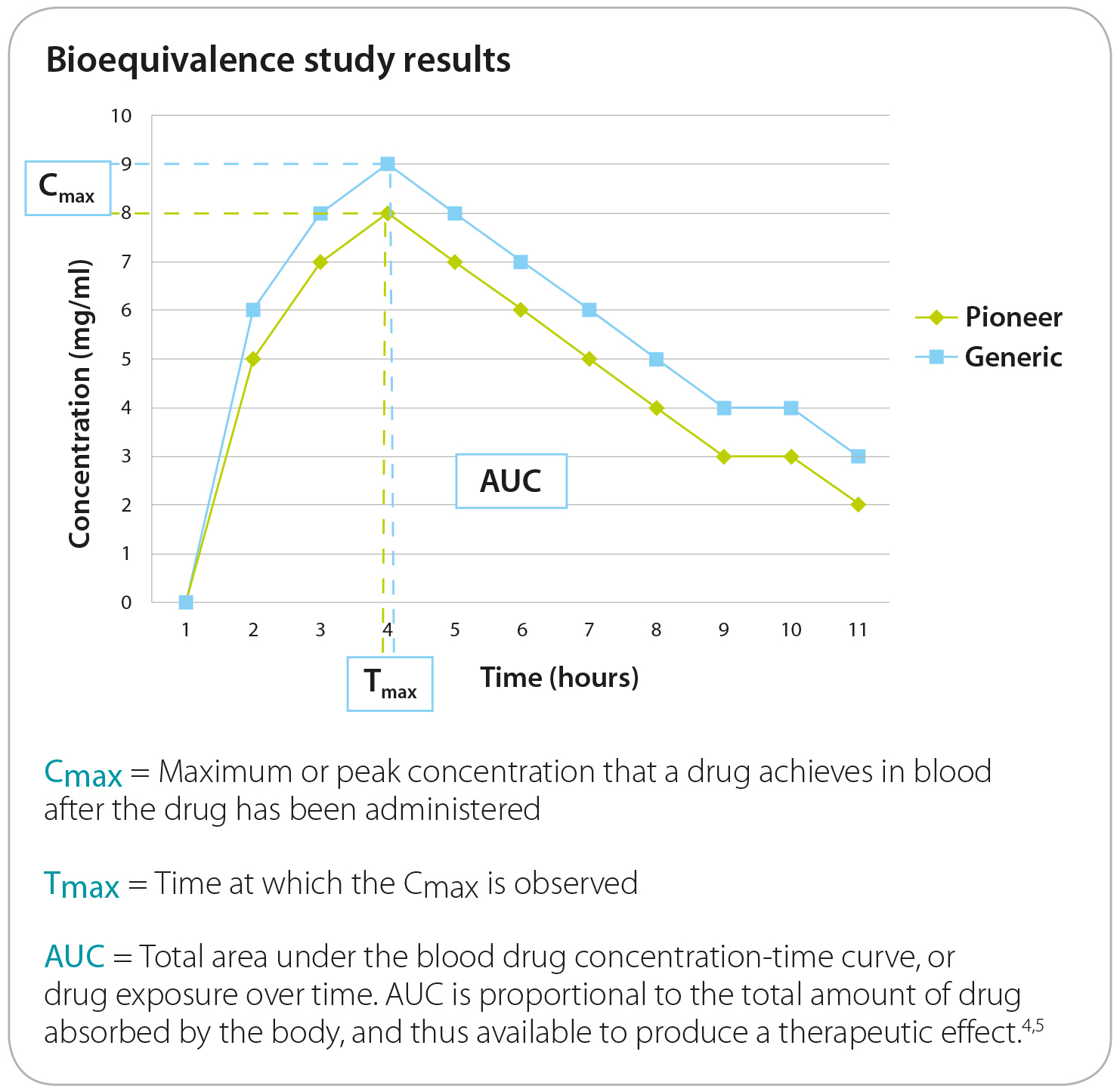
To determine bioequivalence, the generic sponsor completes blood level studies comparing its formulation vs. the pioneer's and reports to what extent the active ingredient concentrates in the blood and and for how long. The average or mean results for the generic product must not be significantly different in comparison to the pioneer product.
The EMA considers two products bioequivalent if the
mean peak concentration (Cmax; the maximum serum concentration that a drug achieves) and the area under the curve (AUC; total exposure over time) are not significantly different when applying a 90% Confidence Interval (CI) approach.The acceptable limits are that the generic product mean must be within the *80%-120% (untransformed data) or 80%-125% (log-transformed data) of the mean of the reference product).
This does not mean that the generic drug is allowed to have 20% less active ingredient that the pioneer. Both products must be formulated to contain the same amount of active ingredient.
To conduct the bioequivalence study, the same dosage is used for both the pioneer and generic formulations. Below is a graph of BE study results illustrating the mean blood concentrations of a pioneer drug (green line) and generic drug (blue line). If the two drugs are deemed to be bioequivalent, the products are considered equivalent and interchangeable.3 .
It is often not just bioequivalence that has to be proven - in some cases target animal safety and residue depletion for consumer safety testing must be carried out and you must always do a user
safety and environmental safety test on generic products. -
-
Should I feel confident with a generic product?
The quality and monitoring processes continue after the generic drug is approved
EMA’s post approval requirements for pioneer drugs and generic drugs are identical:
-
Reporting of manufacturing changes
-
On-going stability testing
-
Pharmacovigilance (adverse event monitoring and reporting)
-
-
References
1 http://www.hma.eu/uploads/media/CMD_v__GUI-014_Processing_generics_
through_MRP-DCP_-_PUBLIC_FINAL-_EMEA-CMDv-262452-2008.pdf2 http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/special_topics/
document_listing/document_listing_000335.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac0580514d5c3 bpac, What is Bioavailability and Bioequivalence? – Generics 2009
4 FDA-CVM bioequivalence guidance #35, November 8, 2006
5 VICH GL52 http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/
GuidanceComplianceEnforcement/GuidanceforIndustry/ucm042450.htm -
Glossary
Pharmaceutical equivalence:
Generic and pioneer products contain exactly the same ingredients in
the same concentration and are manufactured in the same way.Bioequivalence:
Generic and pioneer products have the same active ingredients but may have different excipients or concentration of excipients. In this case, bioequivalence studies are required i.e. tests to ensure that the active reaches the same concentration in the blood for the same duration of time as the pioneer products.


